Headings of Contents
- 1 Python Keywords Tutorial
- 1.1 What is Python Keywords ?
- 1.2 How to get Python Keywords ?
- 1.3 Get Python keywords using help() function:
- 1.4 Information of any particular keyword:
- 1.5 Get Python keywords using keyword module:
- 1.6 Description of Python keywords:
- 1.6.1 True
- 1.6.2 False
- 1.6.3 None
- 1.6.4 and, or, not
- 1.6.5 as
- 1.6.6 assert
- 1.6.7 async, await
- 1.6.8 class
- 1.6.9 def
- 1.6.10 del
- 1.6.11 if, else, elif
- 1.6.12 except, raise, try
- 1.6.13 finally:
- 1.6.14 for
- 1.6.15 from, import
- 1.6.16 global
- 1.6.17 in
- 1.6.18 is
- 1.6.19 lambda
- 1.6.20 nonlocal
- 1.6.21 pass
- 1.6.22 return
- 1.6.23 while
- 1.6.24 with
- 1.6.25 yield
- 1.7 Conclusion:
Python Keywords Tutorial
In this Python keywords tutorial, we are going to learn Python keywords and identifiers. Keywords in Python are reversed words and identifiers is the name given to variables. In the previous tutorial, we have seen Python Variables and their uses.
If you don’t know about Python Variables, Then click here to know about detailed information about Python variables.
Before going through this article. Let’s understand what exactly Python keywords.
What is Python Keywords ?
In Python, keywords are reversed words which means you can not use keyword name as the variable name and function name as well as identifier name. Python provides 33 various types of keywords that are used in different works.
Python keywords are case-sensitive. In this python keywords tutorial, we will see all the python keywords one by one with brief descriptions and examples.
How to get Python Keywords ?
To get Python Python keywords list, we have two methods.
- Using help() function
- Using keyword module
Get Python keywords using help() function:
help() function is a Python built-in function that is used to get the detailed information of any module, function, class, keywords, etc.
To get all the keywords, you have to open your python interpreter and type help(‘keywords’).
Example
help('keywords')Output
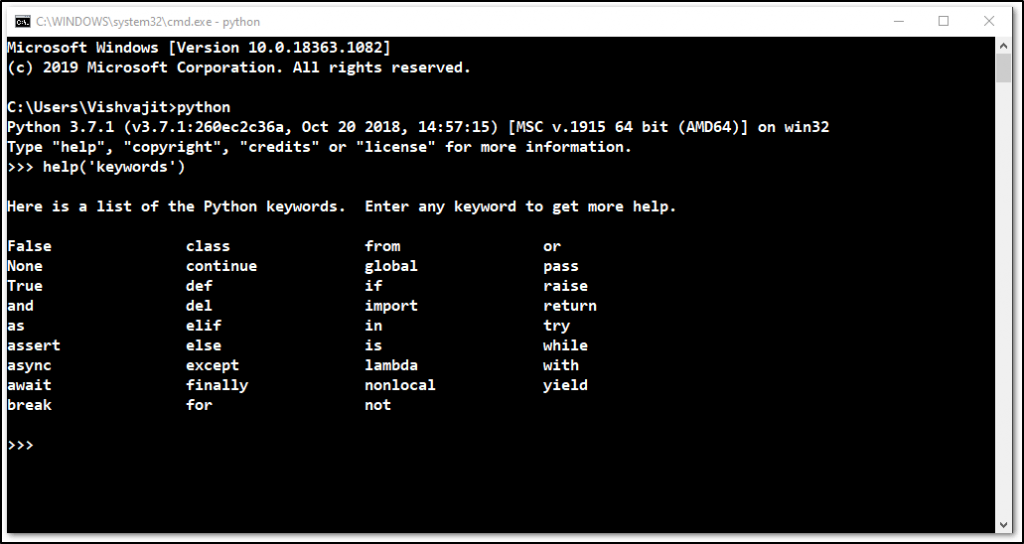
Information of any particular keyword:
To get detailed information of any particular keyword, you can also use the help() function and pass the keyword name inside the function within single or double-quotes.
Example
help('False')Get Python keywords using keyword module:
This is another way to get the information of python keywords. To get the list of all keywords, you can use a keyword built-in module.
Example
import keyword
print(keyword.kwlist)Output
['False', 'None', 'True', 'and', 'as', 'assert', 'async', 'await', 'break', 'class', 'continue', 'def', 'del', 'elif', 'else', 'except', 'finally', 'for', 'from', 'global', 'if', 'import', 'in', 'is', 'lambda', 'nonlocal', 'not', 'or', 'pass', 'raise', 'return', 'try', 'while', 'with', 'yield']Let’s see detailed information of all the Python keywords one by one.
Description of Python keywords:
True
Return True when argument x is true, otherwise False. This is used in comparison operations or logical operations.
>>> 1==1
True
>>> 10>=1
True
>>> True or False
TrueFalse
Return True when x s true, otherwise False. The built-in True and False are two instances of class bool.
>>> 1==2
False
>>> 10<=1
False
>>> True and False
FalseNone
In Python, None is a special constant Python that represents the absence of value or null value. It is the object of its own data type.
>>> x = None
>>> y = None
>>> x==y
Trueand, or, not
and, or and not are the logical operations in Python. and return True when all the conditions separated by an operator return True. or return True when any condition separated by or operator return True. not operator is used to invert the truth value.
>>> 12 > 5 and 5 < 10
True
>>> 12 > 5 or 5 < 2
True
>>> x = 12
>>> not x < 20
Falseas
as keyword is used to assign the alias name of the module during importing of the module.it means you can give another name of the module when importing the module.
>>> from datetime import datetime as dt
>>> dt.now()
datetime.datetime(2020, 9, 27, 16, 18, 58, 832419)assert
assert is used for debugging purposes:
>>> a = 10
>>> assert a > 12
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "<stdin>", line 1, in <module>
AssertionErrorasync, await
async and await keywords provide by the Python asyncio module. async keyword specifies that a function executed asynchronously and await keyword make the program wait for a particular second.
import asyncio
async def do_something():
print('Hello, this is')
await asyncio.sleep(5)
print('Programming Funda')
#To run the above program you have to use below command.
asyncio.run(do_something())Output
Hello, this is
Programming Fundaclass
the class keyword is used to create a user-defined class in Python. class is a collection of attributes and methods.
class Name:
def __init__(self, fname, lname):
self.fname = fname
self.lname = lname
def fullname(self):
print(f"My name is {self.fname} {self.lname}")
#To ruun this program, you have to use following.
x = Name('Vishvajit', 'Rao')
x.fullname()Output
My name is Vishvajit Raodef
def keyword is used to create a user-defined function in Python. In Python function is a block of code which is used to perform a particular task.
def fullname(fname, lname):
print(f"My name is {fname} {lname}")
#To run above function, you have to call the function with parameter by using function name.
fullname('Vishvajit', 'Rao') Output
My name is Vishvajit Raodel
the del keyword is used to delete references to an object.
a = 10
print(a)
del a
print(a)Output
10
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "c:\Users\Vishvajit\Desktop\testing\test.py", line 4, in <module>
print(a)
NameError: name 'a' is not definedif, else, elif
if, else and elif statement is used to with condition statement or decision making.
When you want to test some condition and execute a block of code if the condition is true, Then you can use if and else statement. elif statement is used to execute a block of code when the previous condition is False.
def testing(n):
if n==1:
print('One')
elif n==2:
print('Two')
else:
print('Something else')
testing(1)
testing(2)
testing(5)Output
One
Two
Something elseexcept, raise, try
except, raise and try python keywords are used for exception handling.
try: try block is used to raise the exception.
except: except block is used to handle the exception which is raised by try block.
def testing(n):
try:
result = 1/n
print(result)
except:
print('I have handled the exception')
testing(10)
testing(0)Output
0.1
I have handled the exceptionraise: raise block is used to raise the exception.
finally:
finally, the block is used with try and except block to close the resources or file streams. finally, the block always executes regardless try block. we have a file named test.txt which contains the following text.
test.txt:
This file is created only for demo purposes.
Now we will read all the text from the test.txt file using the open() function and close inside finally block.
def testing():
try:
f= open('test.txt', 'r')
print(f.read())
except:
print('I have handled the exception')
finally:
f.close()
testing()Output
This is only demo purpose.for
for loop is used for looping. for loop is used, When you want to execute a block of code specific number of times.
for i in range(1, 6):
print('Programming Funda.com')Output
Programming Funda.com
Programming Funda.com
Programming Funda.com
Programming Funda.com
Programming Funda.comfrom, import
import keyword is used to import the module in the current namespace.
from keyword is used to import the specific attributes, function, and class from the namespace.
import mathIn the above, we imported the whole math module using the import keyword.
Now are going to import sin() function using from import..from keyword.
>>> from math import sin
>>> print(sin(90))
0.8939966636005579global
In Python, the global keyword is used to create a global variable inside a function.
def message():
global x
x = 'Programming Funda'
print(x)
message()
x = 'hello'
print(x)Output
Programming Funda
helloin
in operator is used to check if the sequence (list, tuple, set ) contains a value or not.
x = [1,2,3,4,5,6,7]
if 5 in x:
print('Well done!')Output
Well done!is
is the operator is used in Python to check object identity? While == is used to check two-variable have the same value or not.
>>> x = [1,2,3,4,5,6,7]
>>> y = [1,2,3,4,5,6,7]
>>> print(x == y)
True
>>> print(x is y)
False
>>> print(True is True)
True
>>> print(False is False)
Truelambda
a lambda function is a single-line anonymous function.
>>> x = lambda x, y: x * y
>>> print(x(12, 23))
276nonlocal
The nonlocal keyword is used to work with variables inside the nested function. Where the variable should not belong to the inner function. Use the nonlocal keyword to declare a variable is not local.
def func1():
x = 'Vishvajit Rao'
def func2():
nonlocal x
x = 'Programming Funda'
func2()
return x
print(func1())Output
Programming Fundapass
In Python, the pass is a null statement. When you don’t want to execute any code inside the function then you can use the pass statement.
def func1():
pass
print(func1())Output
Nonereturn
The return statement is used inside a function to exit and return a single value from a function.
def func1():
return 'Programming Funda'
print(func1())while
while loop is used to execute a block of code a specific number of times.
i = 1
while i < 6:
print('Programming Funda')
i = i + 1Output
Programming Funda
Programming Funda
Programming Funda
Programming Funda
Programming Fundawith
The “with” statement is used to wrap the execution of a block with
methods defined by a context manager.
with open('test.txt','r') as file:
print(file.read())yield
yield python keyword is used to create a generator.
def generator():
for i in range(1, 6):
yield i * i
for i in generator():
print(i)Output
1
4
9
16
25So, we have seen all the keywords in Python in Python with appropriate examples.
Conclusion:
In this Python keywords tutorial, you have learned about Python keywords with descriptions and examples.
I think you have not any confusion regarding Python keywords. Python keywords are reversed words that mean you can not assign variable, function name, class name, and identifier with Python keywords.
If this post helped you, please share it with your friends who want to learn Python programming from scratch to advanced.