Hello Python programmer, In this guide, we will go through the Python super() function using examples. super function in Python is a powerful function to give access to the method and properties of parent or base class.
The super function gives us the authority to ignore the base class name to call its attributes and methods from the child class or derived class.
Headings of Contents
Python super function
Python super() function is used to access all the methods and properties from the base class or parent class. super() function return an object that represents the parent class.
In Python, super() has two major use cases:
- super() function us to avoid using the base class name explicitly
- super() working with Multiple Inheritance
Syntax
The syntax of the super function in Python is:-
super()Parameter
super function in Python does not support any parameter.
Return Type
The super function returns a proxy object which represents the parent class.
Python super function example
Here, we will go through with super function in Python with the help of different-different examples so that you don’t have any confusion regarding Python super function and its use cases.
How does Inheritance work without super
In this example, we will not use the super() function and try to access the property of the parent class from the object of the child class. let’s see what happens.
class Employee:
def __init__(self):
self.name_ = 'John'
self.role = 'Programmer'
class Person(Employee):
def __init__(self):
self.var = 'Instance variable in B'
self.name = 'Vishvajit'
self.role = 'Student'
p1 = Person()
print("Child class attribute:- ", p1.name)
print("Parent class attribute:- ", p1.name_)After successfully the above code, the output will be:
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "C:\Users\Vishvajit Rao\OneDrive\Desktop\Pyspark\main.py", line 94, in <module>
print("Parent class attribute:- ", p1.name_)
AttributeError: 'Person' object has no attribute 'name_'. Did you mean: 'name'?
Child class attribute:- VishvajitAs you can see in the above output, the Child class attribute name was successfully accessed but in the case of the Parent class name_ attribute, an AttributeError exception has been raised. That’s the problem.
To solve this type of problem, super function comes into the picture. Let’s see how can we solve this problem using the super() function.
class Employee:
def __init__(self):
self.name_ = 'John'
self.role = 'Programmer'
class Person(Employee):
def __init__(self):
self.var = 'Instance variable in B'
self.name = 'Vishvajit'
self.role = 'Student'
super().__init__()
p1 = Person()
print("Child class attribute:- ", p1.name)
print("Parent class attribute:- ", p1.name_)Output
Child class attribute:- Vishvajit
Parent class attribute:- JohnNow you can see attributes of child class and parent class have been accessed.
Using Base class name:
Using base class meaning Employee, you can access or inherit the method and properties of the parent class or base class.
class Employee:
def __init__(self):
self.name = 'John'
self.role = 'Programmer'
class Doctor(Employee):
def __init__(self):
self.var = 'Instance variable in B'
self.name = 'Vishvajit'
self.role = 'Student'
Employee.__init__(self)
x = Doctor()
print(x.var)
print(x.name)
print(x.role)Output
Instance variable in B
John
ProgrammerAs you can see in the above Output, we have successfully accessed the value of the name and role of the parent class. So this is how you can use the Base class name to access or inheritance the properties and methods from the base class.
Without using the super function:
In this example, I am not going to use the super() function and the Base class name and still will try to access the properties from the Base class or Parent class.
Let’s see what heppens.
class Employee:
def __init__(self):
self.name = 'John'
self.role = 'Programmer'
class Doctor(Employee):
def __init__(self):
self.var = 'Instance variable in B'
self.name = 'Vishvajit'
self.role = 'Student'
x = Doctor()
print(x.var)
print(x.name)
print(x.role)Output
Instance variable in B
Vishvajit
Student As you can see in the output, I am not able to access the properties from the parent class this is because the __init__() method of the child class overrides the __init__() method of the parent class.
With using super() function:
class Employee:
def __init__(self):
self.name = 'John'
self.role = 'Programmer'
class Doctor(Employee):
def __init__(self):
self.var = 'Instance variable in B'
self.name = 'Vishvajit'
self.role = 'Student'
super().__init__()
x = Doctor()
print(x.var)
print(x.name)
print(x.role) Output
Instance variable in B
John
ProgrammerIn the above example, we called the __init__() method of the Employee class from the Doctor class using super.__init__() instead of using Employee.__init__().
Since we don’t need to specify the base class name to call its methods and properties. We can easily call the base class methods and properties by using the super() function.
super() function with Multilevel Inheritance:
In all the above examples, we have seen almost Multiple inheritances to use the super function but still, I am going to give you a brief example of Python multilevel inheritance along with super() function implementation.
Multilevel Inheritance:- In multilevel inheritance, A class can also be derived or inherited from another derived class and base class which means a class that features the base class and child class is also inherited from another child class.
As you can see below image.
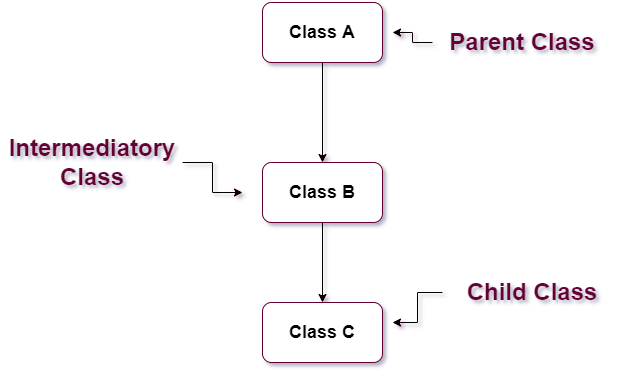
Example: Using the super() function in Multilevel Inheritance
class Person:
def __init__(self, name1):
print(name1 , " is person")
class Doctor(Person):
def __init__(self, name2):
print(name2, "is doctor")
super().__init__(name2)
class Engineer(Doctor):
def __init__(self, name3):
print(name3, "is Engineer")
super().__init__(name3)
x = Engineer('Vishvajit')Output
Vishvajit is Engineer
Vishvajit is doctor
Vishvajit is personsuper() function with Multiple Inheritance
The super() function is also used with multiple inheritances. In this example, I will inherit a method of both parent classes ( Father and Mother ) from its child class named Son. So this is how you can use the super() function in Multiple inheritances.
Multiple Inheritance:- In multiple Inheritance, a child class inherited or derived from more than one base class or parent class.
As you can see. Class C is inherited or derived from both Class A and Class B.
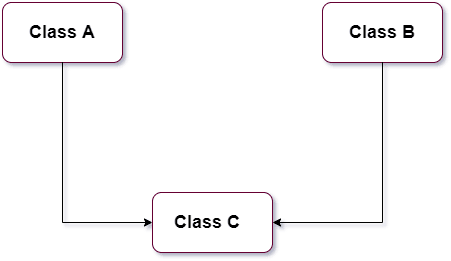
Example: Using the super() function in Multiple Inheritance
class Father:
def father_name(self):
print("My Father name is:- ABC")
class Mother:
def mother_name(self):
print("My Mother name is:- XYZ")
class Son(Mother, Father):
def display(self):
print("My name is:- abc xyz")
super().father_name()
super().mother_name()
s1 = Son()
s1.display()Output
My name is:- abc xyz
My Father name is:- ABC
My Mother name is:- XYZConclusion
In this article, you have learned Python super function along with examples. The super function is the best built-in function to access the base class attributes and methods. You have to remember one thing, The super() function always returns a proxy object which represents the parent class.
If you’ll work with Inheritance in Python, you can’t ignore Python super function.
Python built-in functions
For more information:- Click Here
Thanks for your valuable time … 🧑💻🧑💻🙏